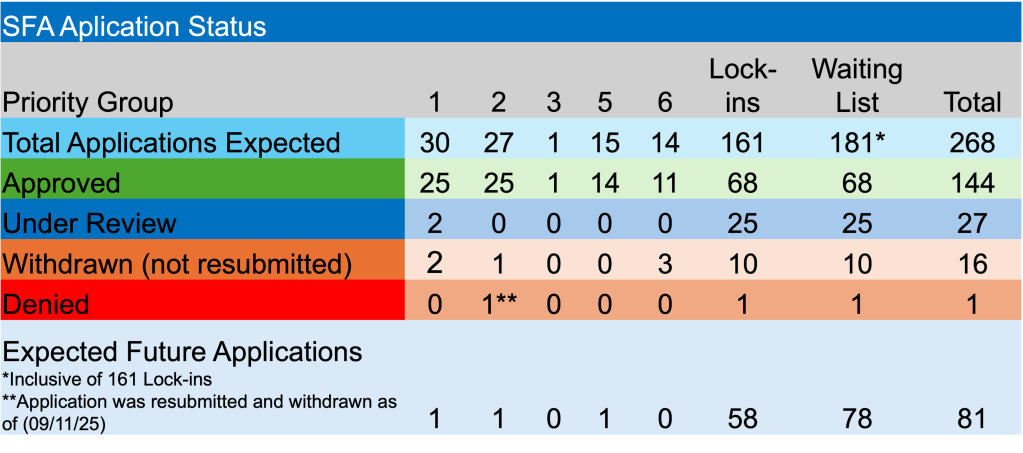
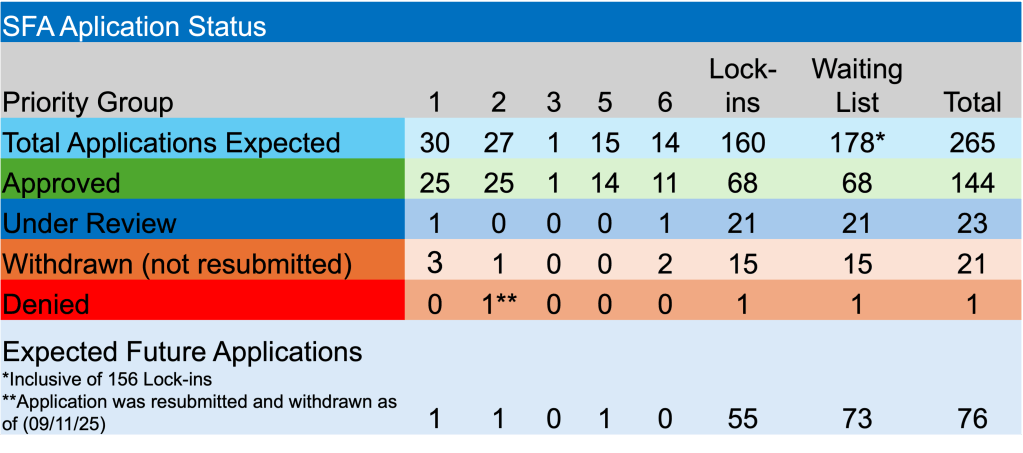
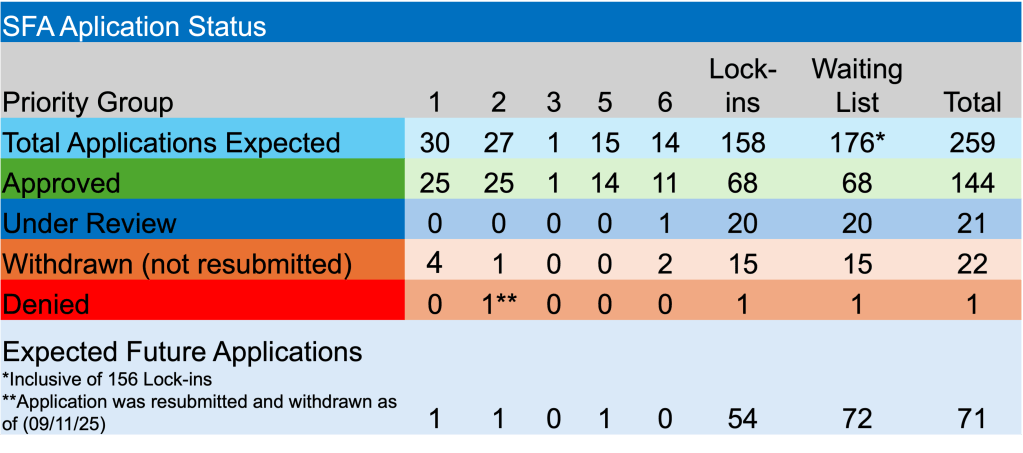
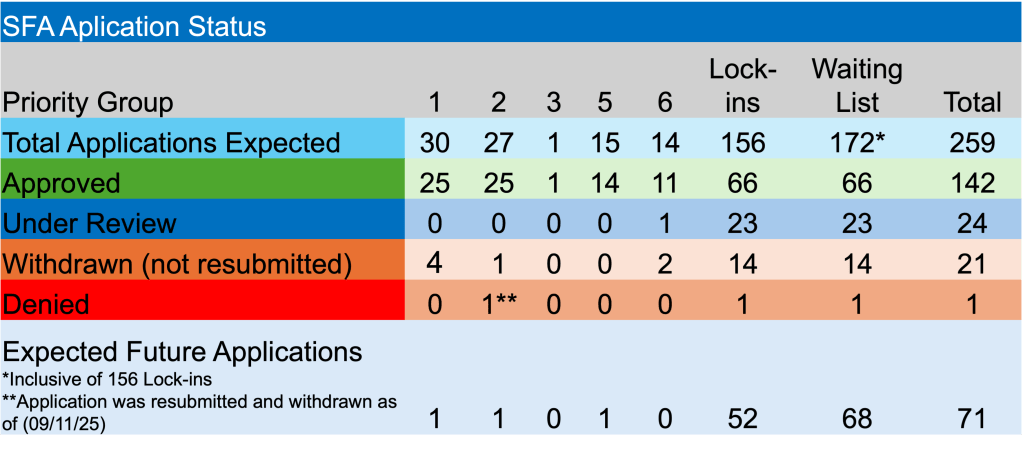
By: Russ Kamp, CEO, Ryan ALM, Inc.
Imagine a world, or at least the United States, where pension plans are no longer subject to market swings and the uncertainty those swings create. What if you could “guarantee” (outside of any corporate bond defaults) the promises made to your plan participants, ensuring their financial security with confidence? In today’s highly unpredictable investing environment, relying solely on the pursuit of investment returns is a risky ride—one that guarantees volatility and sleepless nights but not necessarily success. It’s time to rethink how we manage defined benefit (DB) pension plans and embrace a strategy that brings true certainty: Cash Flow Matching (CFM). Discover through the hypothetical conversation below how CFM can transform your investing approach, protect your plan, and deliver peace of mind for everyone involved. Let’s go!
Why are we talking about Cash Flow Matching (CFM) today?
First off, thanks for taking a few minutes to chat with me. As you may have heard me say before, our mission at Ryan ALM, Inc. is simple — to protect and preserve defined benefit (DB) pension plans and to secure the promises made to participants.
We believe that Cash Flow Matching (CFM) is one of the few strategies that can help us keep those promises with real certainty.
Why Now?
Because the world feels more uncertain than ever.
And if we’re honest, most of us don’t like uncertainty. Yet somehow, in the pension world, many plan sponsors have gotten used to it. Why is that?
Over the years, we’ve been taught that managing a DB plan is all about chasing returns. But that’s not really the case. When a plan invests 100% of its assets purely with a return objective, it locks itself into volatility — not stability or success.
That approach also puts your plan on the “asset allocation rollercoaster,” where markets rise and fall, and contributions swing higher and higher along with them. It’s time to step off that ride — at least for part of your portfolio.
So if it’s not all about returns, what is the real objective?
Managing a DB pension plan is all about cash flows — aligning the cash coming in (from principal and interest on bonds) with the cash going out (for benefits and expenses).
The real goal is to secure those promised benefits at a reasonable cost and with prudent risk. That’s the foundation of a healthy plan.
Does bringing more certainty mean I have to change how I manage the plan?
Yes — but only a little. The adjustments are modest and easy to implement.
How can I adopt a CFM strategy without making major changes?
The first step is to reconfigure your asset allocation. Most DB plans are currently 100% focused on returns. It’s time to split your assets into two clear buckets:
- Liquidity bucket – designed to provide cash flow to pay benefits and expenses.
- Growth bucket – focused on long-term return potential.
What goes into the liquidity bucket?
Most plans already hold some cash and core fixed income. Those assets can move into the liquidity bucket to fund benefit payments and expenses.
And what happens with the remaining assets?
Nothing changes there. Those assets stay in your growth or alpha bucket. The difference is that you’ll no longer need to sell from that bucket during market downturns, which helps protect your fund from the negative impact of forced selling.
Is that all I need to do to create more certainty?
Not quite. You’ll also want to reconfigure your fixed income exposure.
Instead of holding a generic, interest-rate-sensitive bond portfolio (like one tied to the Bloomberg Aggregate Index), you’ll want a portfolio that matches your plan’s specific liabilities — using both principal and income to accomplish the objective.
That’s where true cash flow matching comes in.
How does the matching process work?
We start by creating a Custom Liability Index (CLI) — a model of your plan’s projected benefit payments, expenses, and contributions. This serves as the roadmap for funding your monthly liquidity needs.
What information do you need to build that index?
Your plan’s actuary provides the projected benefits, expenses, and contributions as far out into the future as possible. The more data we have, the stronger the analysis. From there, we can map out your net monthly liquidity needs after accounting for contributions.
Which bonds do you use to match the cash flows?
We invest primarily in U.S. Treasuries and U.S. investment-grade corporate bonds. We stick with these because they provide dependable cash flows without introducing currency risk.
We limit our selections to bonds rated BBB+ or higher, and the longest maturity we’ll buy matches the length of the mandate. For example, if you ask us to secure 10 years of liabilities, the longest bond we’ll buy will mature in 10 years.
Do you build a laddered bond portfolio?
No — a traditional ladder would be inefficient for this purpose.
Here’s why: the longer the maturity and the higher the yield, the lower the overall cost of funding those future liabilities. So instead of a simple ladder, we use a proprietary optimization process to build the portfolio in a way that maximizes efficiency and minimizes cost.
It sounds manageable — not a big overhaul. Am I missing something?
Not at all. That’s exactly right.
Dividing assets into liquidity and growth buckets and reshaping your bond portfolio into a CFM strategy is typically all that’s required to bring more certainty to part of your plan.
Every plan is unique, of course, so each implementation will reflect its own characteristics. But generally speaking, CFM can reduce the cost of future benefits by about 2% per year — or roughly 20% over a 10-year horizon.
On top of that, it helps stabilize your funded status and contribution requirements.
How much should I allocate to CFM?
A good starting point is your existing cash and bond allocation. That’s the least disruptive way to begin.
Alternatively, you can target a specific time horizon — for example, securing 5, 7, or 10 years of benefits. We’ll run an analysis to show what asset levels are needed to meet those payments, which may be slightly more or less than your current fixed income and cash allocations.
Once implemented, do I just let the liquidity bucket run down?
Most clients choose to rebalance annually to maintain the original maturity profile. That keeps the strategy consistent over time. Of course, the rebalancing schedule can be customized to your plan’s needs and the broader market environment.
This all sounds great — but what does it cost?
In line with our mission to provide stability at a reasonable cost and with prudent risk, our fee is about half the cost of a typical core fixed income mandate.
If you’d like, we can discuss your specific plan details and provide a customized proposal.
Final thoughts
Thank you for taking the time to explore CFM. Many plan sponsors haven’t yet heard much about it, but it’s quickly becoming a preferred approach for those who value stability and peace of mind.
At the end of the day, having a “sleep well at night” strategy benefits everyone — especially your participants.