By: Russ Kamp, Managing Director, Ryan ALM, Inc.
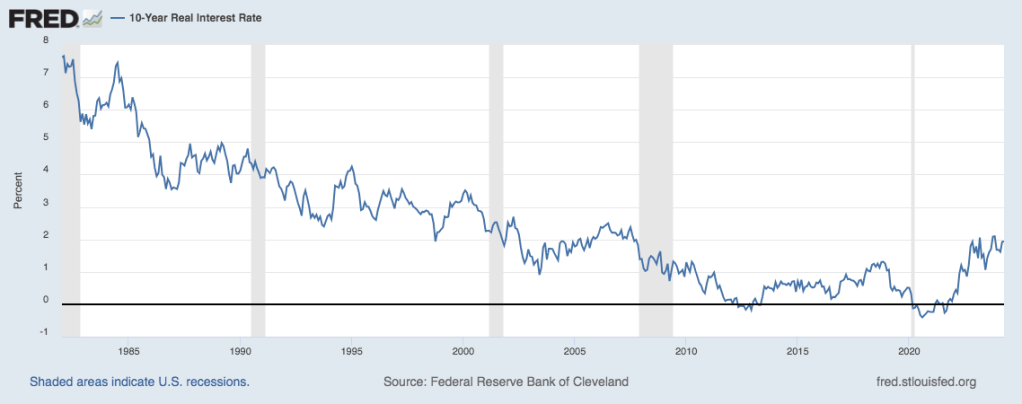
A traditional DB plan’s asset allocation comes with a lot of annual volatility (see the graph below). That volatility gets reduced as one extends the investing horizon, but it is still quite uncertain until you extend sufficiently, such as 10 or more years. However, as plan sponsors and investment managers, we have been living in a quarter-to-quarter measurement cycle for decades. In that environment, a 1 standard deviation (1 SD) measurement for a 1-year time frame (Ryan ALM asset allocation model since 1999) is +/- 10.5%. In the example below, 68% of the observations (1 SD) will fall between 16.5% and -4.5%. A 2 SD measurement would have the range for 95% of the observations between 27% and -15%. That gap, or should I say canyon, is a 1-year observation. Extend the measurement period to 5-years and the range of results is still wide but less so at +/- 9.8% for 2 SDs. It isn’t until you get beyond 10 years that the volatility associated with a fairly traditional asset allocation gets to a reasonable level.
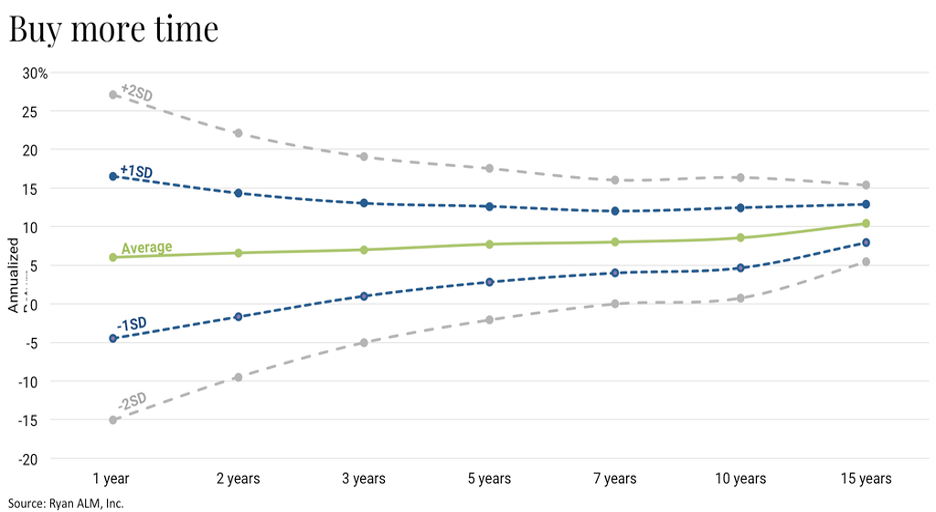
Is there a way to bring more certainty to the asset allocation process that would allow for longer observation periods and less volatility? Absolutely! A plan sponsor and their advisors can adopt a bifurcated asset allocation in which a liquidity bucket is created that will fund and match the plan’s liability cash flows of benefits and expenses chronologically from the next month as far out as the allocation will cover (10+ years) allowing for the remainder of the alpha assets (all non-bond assets) to now grow unencumbered. The task for those assets is to meet future liabilities.
As the graph below highlights, a carefully constructed cash flow matching (CFM) portfolio can help plan sponsors wade through the volatility associated with shorter timeframes. The CFM portfolio will consist of investment grade bonds whose cash flows of interest and principal will be matched to the liability cash flows. This process now ensures (absent defaults) that the necessary liquidity is available when needed as those future promises have been SECURED. The remaining assets can now be managed as aggressively as the plan’s funded status dictates.
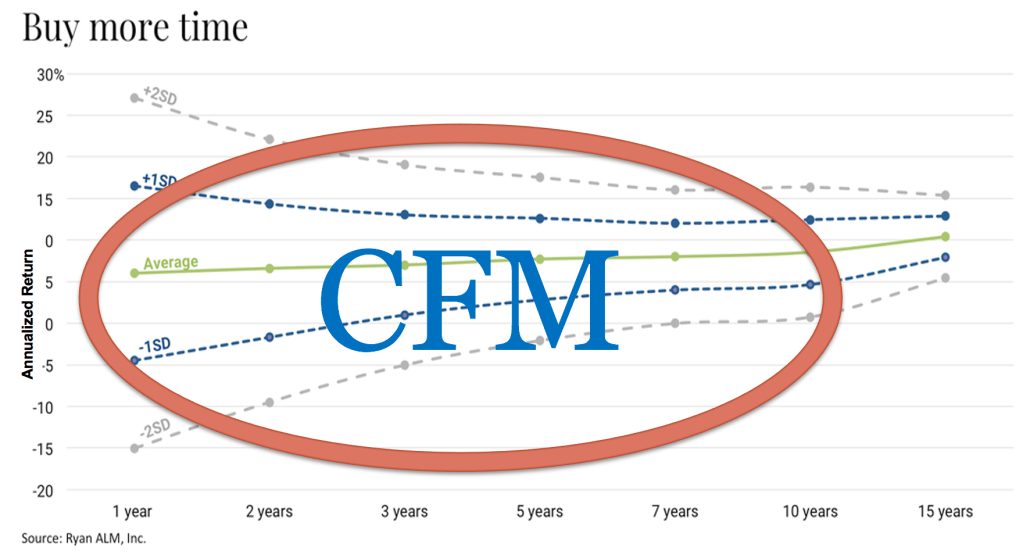
With this process, short-term market dislocations will no longer impact the plan’s ability to meet its obligations. There will be no forced selling to meet benefit payments. The alpha assets can now grow without fear of being sold at an unreasonable level. The CFM program takes care of your needs while establishing a buffer (longer investing horizon) from market corrections that happen on a fairly regular basis. This structure should also lead to less volatility related to contributions and the plan’s funded status.
Given the elevated US interest rate environment, now is the time to engage in this process. CFM will provide a level of certainty that doesn’t exist in a traditional asset allocation. This is a “sleep well at night” strategy that should become the core holding for DB pensions. As I mentioned in an earlier blog post today, bonds should only be used for the cash flows they produce. They should not be used as total return-seeking instruments. Leave that task to the alpha assets that will benefit from a longer investing period.