By: Russ Kamp, CEO, Ryan ALM, Inc.
As I was contemplating my next blog post, I took a look at how many of my previous >1,625+ posts mentioned currencies, and specifically the U.S. $. NEVER had I written about the U.S. $ other than referencing the fact that we enjoy the benefit of a fiat currency. I did mention Bitcoin and other cryptos, but stated that I didn’t believe that they were currencies and still don’t. Why mention them now? Well, the U.S. $ has been falling relative to nearly all currencies for most of 2025. According to the WSJ’s Dollar Index (BUXX), the $ has fallen by 8.5% for the first half of 2025.
Relative to the Euro, the $ has fallen nearly 14% and the trend isn’t much better against the Pound (-9.6%) and the Yen (-8.7%). So, what are the implications for the U.S. given the weakening currency? First, the cost of imports rises. When the $ loses value, it costs more to buy goods and services from abroad. The likely outcome is that the increased costs get passed onto the consumer, who is already dealing with the implications from uncertain tariff policies.
Yes, exports become cheaper, which would hopefully increase demand for our goods, but the heightened demand could also lead to greater demand for U.S. workers in order to meet that demand leading to rising wages (great), but that is also potentially inflationary.
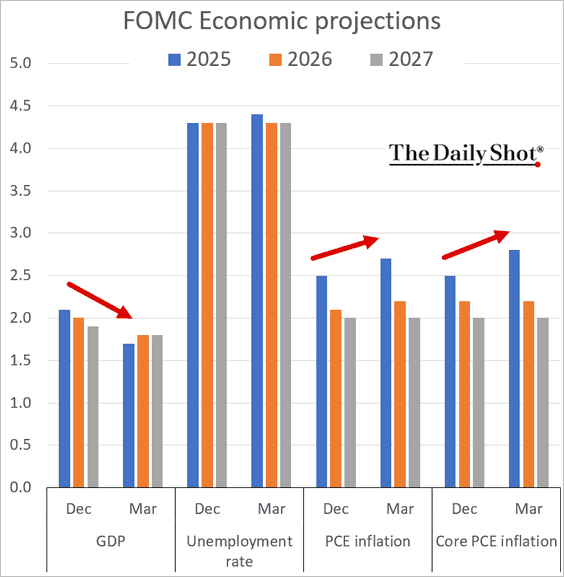
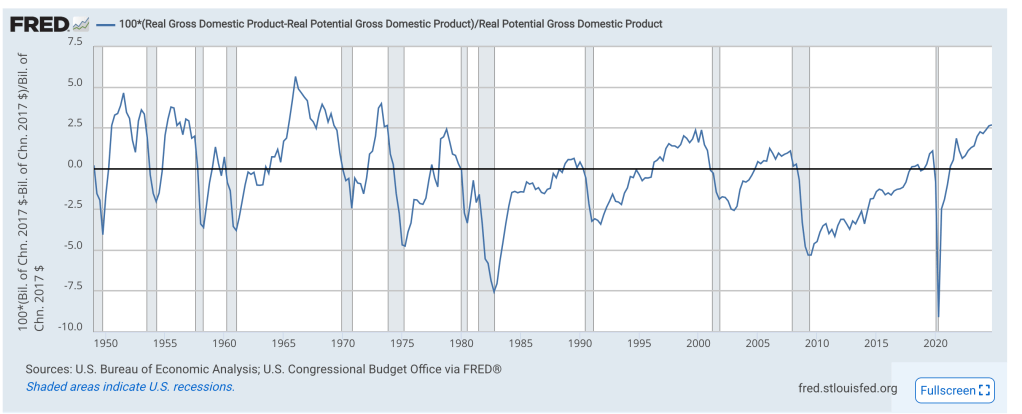
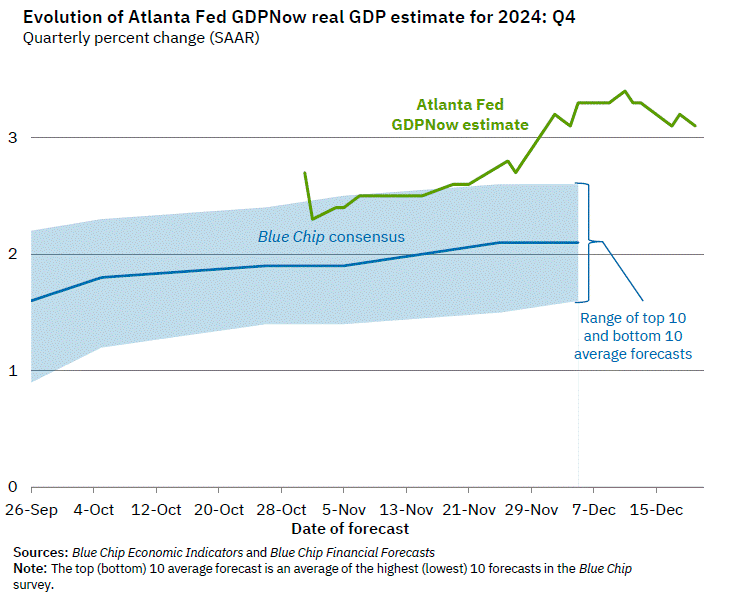
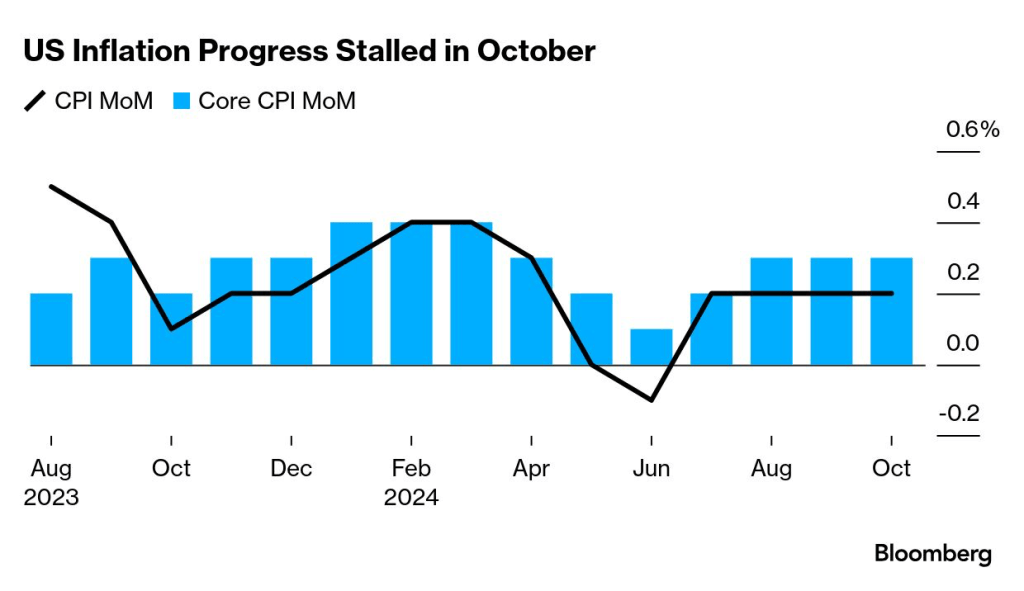
What have we seen so far? Well, first quarter’s GDP (-0.5%) reflected an increase in imports spurred on by fear of price increases due to the potential for tariffs. Q2’25 is currently forecasted to be 2.5% according to the Atlanta Fed’s GDPNow model, as U.S. imports have fallen. According to the BLS, import prices have risen in 4 of 5 months in 2025, with March’s sharp decline the only outlier.
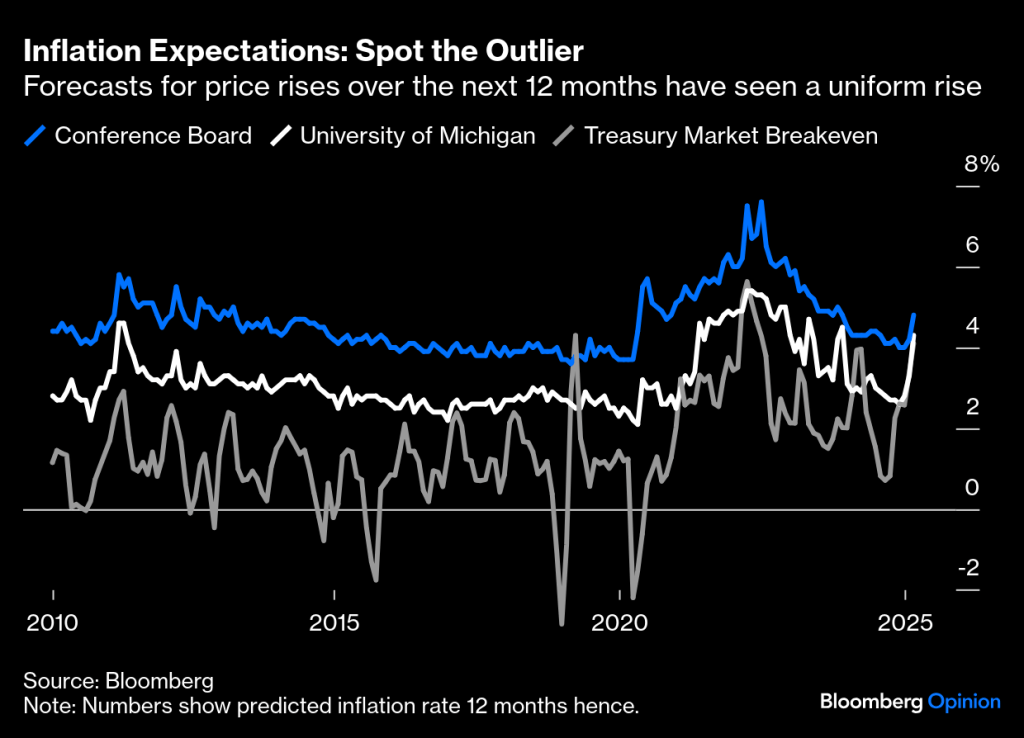
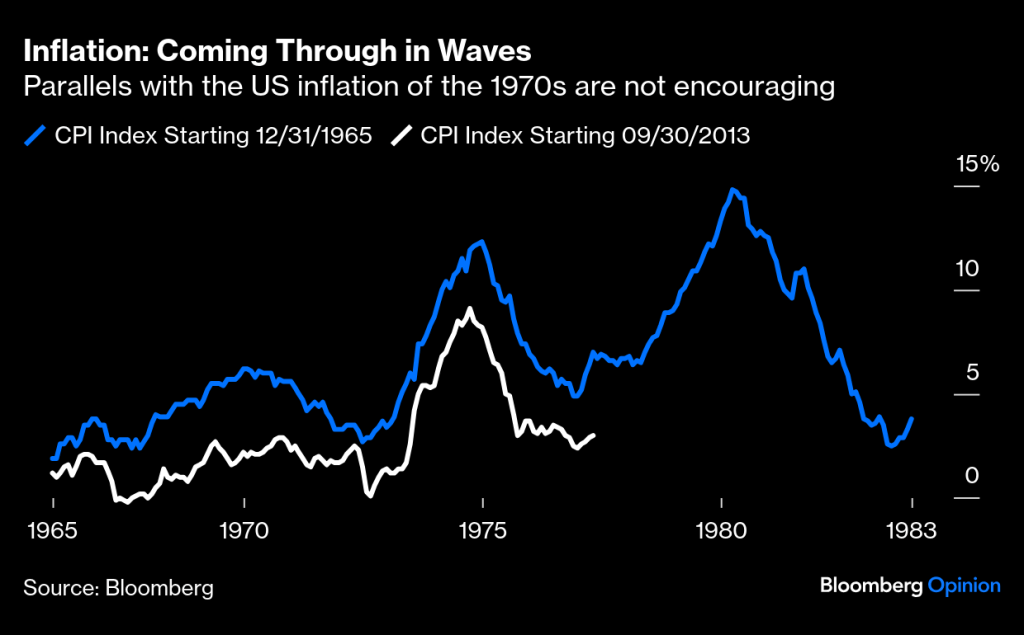
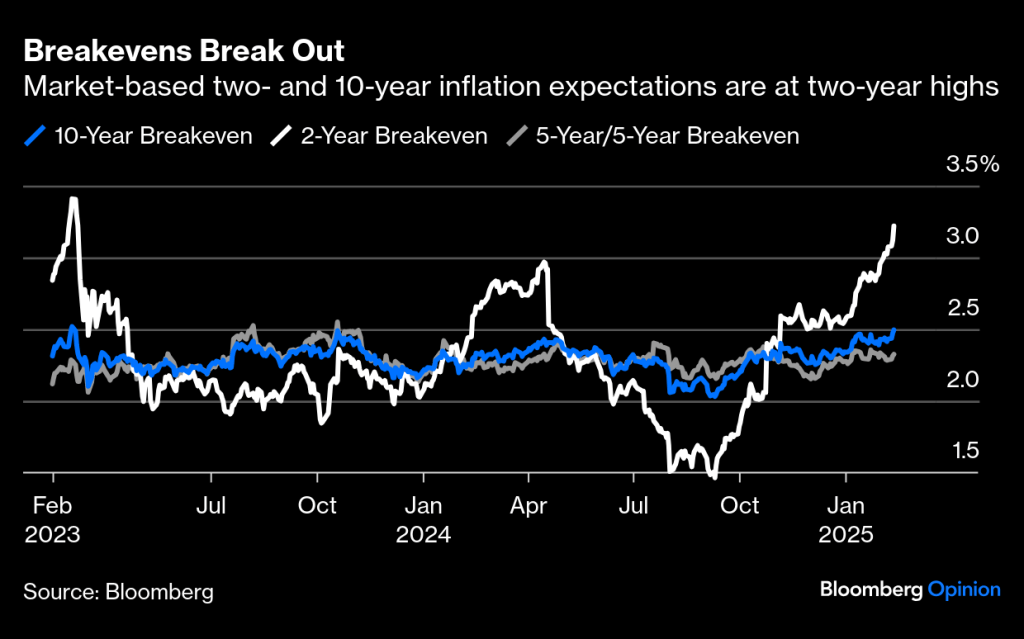
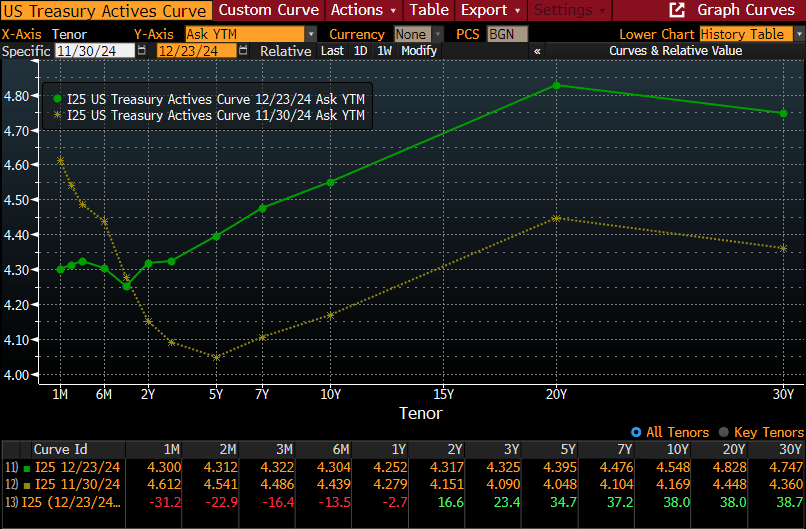
The potential inflationary impact from rising costs could lead to higher U.S. interest rates, which have been swinging back and forth depending on the day of the week and the news cycle. Furthermore, there is fear that the proposed “Big Beautiful Bill” could also drive rates higher due to the potential increase in the federal deficit by nearly $5 trillion due to the stimulative nature of deficits. Obviously, higher U.S rates are great for individual savers, but they don’t help bonds as principal values fall.
We recommend that plan sponsors and their advisors use bonds for the cash flows (interest and principal) and not as a performance driver. Use the fixed income exposure as a liquidity bucket designed to meet monthly benefits and expenses through the use of Cash Flow Matching (CFM), which will orchestrate a careful match of asset cash flows funding the projected liabilities cash flows. The remaining assets (alpha bucket) now benefit from time, as the investment horizon is extended.
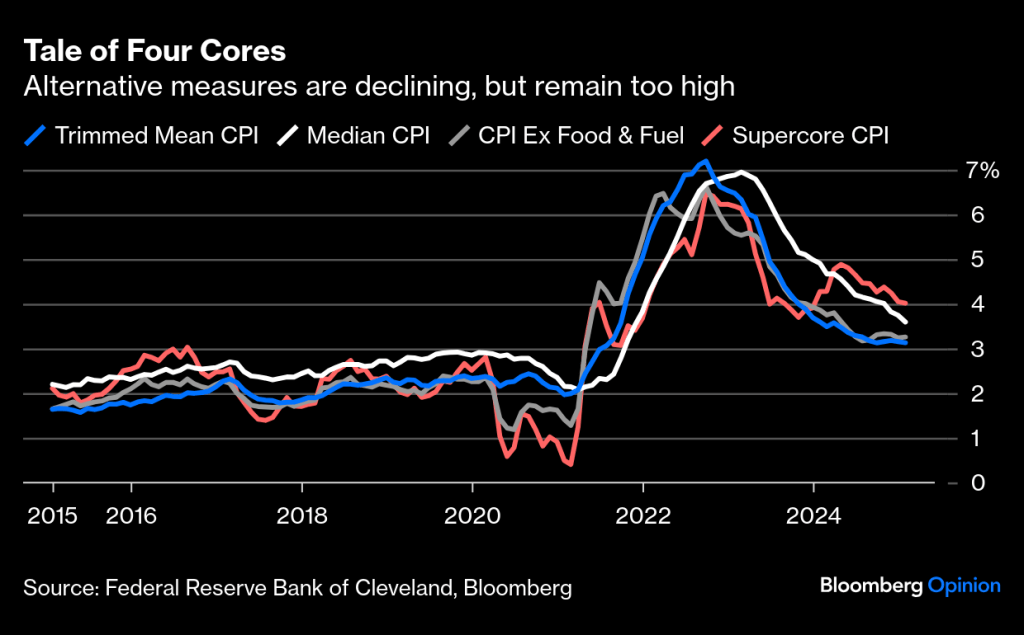
Price increases on imports due to a weakening $ can impact U.S. inflation, but there are other factors, too. I’ve already mentioned tariffs and wage growth, but there other factors, including productivity and global supply chains. Some of these drivers may take more time to hash out. There are many uncertainties that could potentially impact markets, why not bring an element of certainty to your pension fund through CFM.