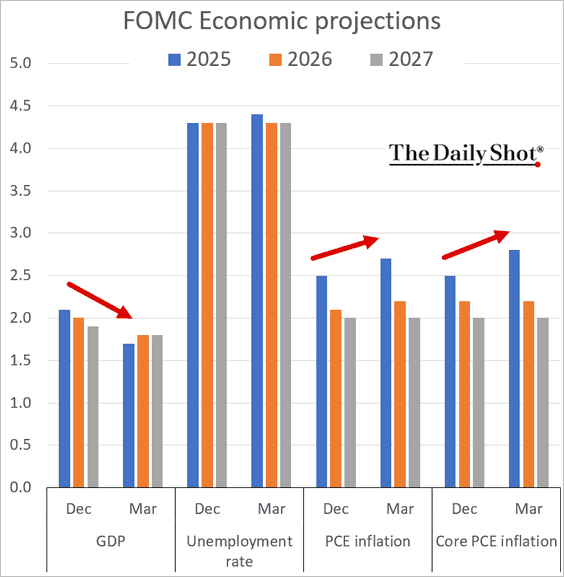
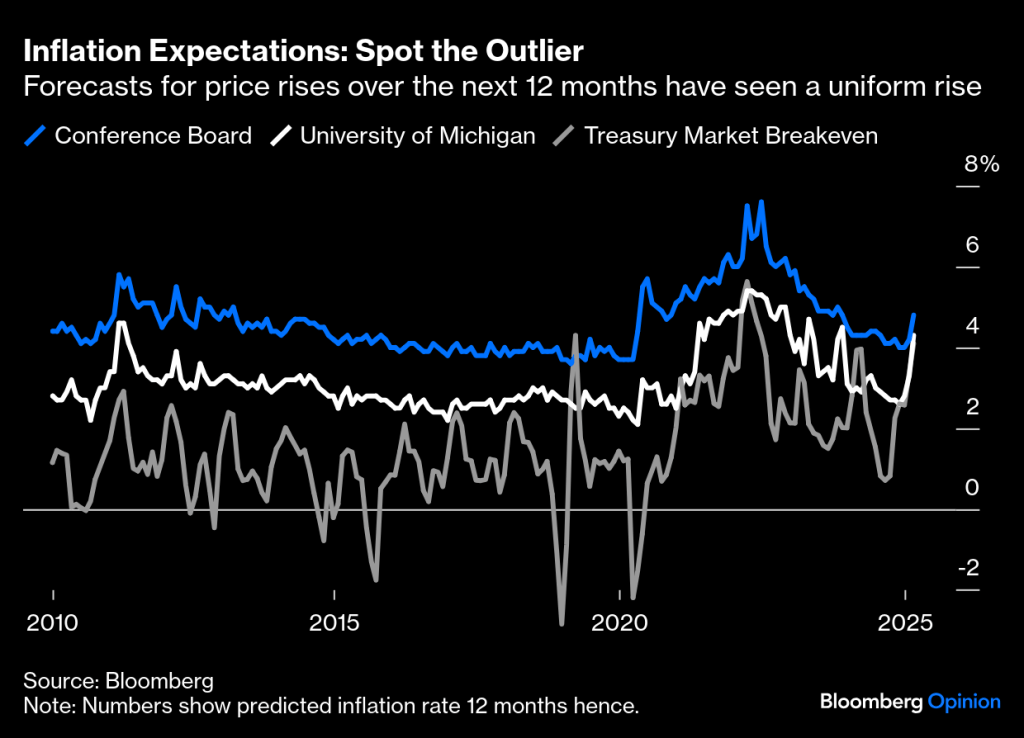
By: Russ Kamp, CEO, Ryan ALM, Inc.
This post may be familiar to some of you, as I originally published it in October 2024. Given today’s great uncertainty related to geopolitics, markets, and the economy, I thought it relevant to share once again. Please don’t hesitate to reach out to me if you want to challenge any part of this list. We always welcome your feedback.
The four senior members at Ryan ALM, Inc. have collectively more than 160 years of pension/investment experience. We’ve lived through an incredible array of markets during our tenures. We have also witnessed many attempts on the part of Pension America to try various strategies to meet the promises that have been made to the pension plan participants.
Regrettably, defined benefit (DB) pension plans continue to be tossed aside by corporate America in favor of defined contribution (DC) plans. Both public and multiemployer plan sponsors would be wise to adopt a strategy that seeks more certainty to protect and preserve these critically important retirement vehicles before they are subject to a similar fate.
We’ve compiled a list of DB pension “Absolute Truths” that we believe return the management of pension plans back to its roots when SECURING the promised benefits at a reasonable cost and with prudent risk was the primary objective. The dramatic move away from the securing of benefits to the arms race focused on the return on asset assumption (ROA) has eliminated any notion of certainty in favor of far greater variability in likely outcomes.
Here are the Ryan ALM DB Truths:
- Defined Benefit (DB) pension plans are the best retirement vehicle!
- They exist to fulfill a financial promise that has been made to the plan participant upon retirement.
- The primary objective in managing a DB plan is to SECURE the promised benefits at a reasonable cost and with prudent risk.
- The promised benefit payments are liabilities of the pension plan sponsor.
- Liabilities need to be measured, monitored, and managed more than just once per year.
- Liabilities are future value (FV) obligations – a $1,000 monthly benefit is $1,000 no matter what interest rates do. As a result, they are not interest rate sensitive.
- Pension inflation is not equal to the CPI but a rate unique to each plan sponsor.
- Best way to hedge pension inflation is through Cash Flow Matching (CFM) since inflation is in the actuarial projections
- Plan assets (stocks, bonds, real estate, etc.) are present value (PV) or market value (MV) calculations. We do not know the FV of assets except for bonds cash flows (interest and principal at maturity).
- To measure and monitor the funded status, liabilities need to be converted from FV to PV – a Custom Liability Index (CLI) is absolutely needed.
- A discount rate is used to create a PV for liabilities – ROA (publics), ASC 715 (corps), STRIPS, etc.
- Liabilities are bond-like in nature. The PV of future liabilities rises and falls with changes in the discount rate (interest rates).
- The nearly 40-year decline in US interest rates beginning in 1982 crushed pension funding, as the growth rate for future liabilities far exceeded the growth rate of assets.
- The allocation of plan assets should be separated into two buckets – Liquidity (beta) and Growth (alpha).
- The liquidity assets should consist of a bond portfolio that matches (defeases) asset cash flows with the plan’s liability cash flows (benefits and expenses (B&E)).
- This task is best accomplished through a CFM investment process.
- The liquidity assets should be used to fund B&E chronologically buying time for the alpha assets to grow unencumbered in their quest to meet those faraway future liabilities not yet defeased by the liquidity assets.
- The Growth assets will consist of all non-bonds, which can now grow unencumbered, as they are no longer a source of liquidity. Growth assets will fund those remaining future liabilities not yet defeased by the liquidity assets.
- The Return on asset (ROA) assumption should be a calculated # derived through an Asset Exhaustion Test (AET)
- The pension plan’s asset allocation should be responsive to the plan’s funded status and not the ROA.
- As the funded status improves, port alpha (profits) from the Growth portfolio into the Liquidity bucket (de-risk) extending the cash flow matching assignment and securing more promises.
- This de-risking ensures that plans don’t continue to ride the asset allocation rollercoaster leading to volatile contribution costs.
- DB plans are a great recruiting and retention tool for managing a sponsor’s labor force.
- DB plans need to be protected and preserved, as asking untrained individuals to fund, manage, and then disburse a “benefit” through a Defined Contribution plan is poor policy.
- Unfortunately, doing the same thing over and over and over is not working. A return to pension basics is critical.
You’ve made a promise: measure it – monitor it – manage it – and SECURE it…
Get off the pension funding rollercoaster – sleep well!