By: Russ Kamp, CEO, Ryan ALM, Inc.
We hope that you’ll agree that going to Chicago in January demonstrates the lengths that Ryan ALM personnel will go to help plan sponsors and their advisors protect and preserve DB pension plans. We are just thankful that we left yesterday, as today’s temperature is not expected to get to 0. OUCH!
Ron Ryan and I spent the last couple of days speaking with a number of funds and consultants about the many benefits of cash flow matching (CFM), which is gaining incredible traction among pension sponsors of all types. Who doesn’t want an element of certainty and enhanced liquidity within their plans given all the uncertainty we are facing in markets and geopolitically.
The idea of creating an element of certainty within the management of pension plans sounds wonderful, but how is that actually achieved? This is a question that we often receive and this trip was no exception. We had been discussing the fact that the relationship between asset cash flows (bond principal and interest) and liability cash flows (benefits and expenses) is locked in on the day that the bond portfolio is produced. The optimization process that we created blends the principal and interest from multiple bonds to meet the monthly obligations of benefits and expenses with an emphasis on longer maturity and higher yielding bonds to capture greater cost reduction of those future promises.
However, to demonstrate how one defeases a future liability, my example below highlights the matching of one bond versus one future $2 million 10-year liability. In this example from 18-months ago we purchased:
Bond: MetLife 6.375% due 6/15/34, A- quality, price = $107.64
Buy $1,240,000 par value of MetLife at a cost = $1,334,736
Interest is equal to the par value of bonds ($1,240,000) times the bond’s coupon (6.375%)
As a result of this purchase, we Receive:
Interest = $78,412.50 annually ($39,206.25 semi-annual payments)
Total interest earned for 10 years is $784,125
Principal = $1,240,000 at maturity (par value)
Total Cash Flow = $2,024,125 – $2,000,000 10-year Liability = $24,124.99 excess
($24,124.99 excess Cash Flow)
Benefits:
Able to fund $2 million benefit at a cost of $1.335 million or a -33.25% cost reduction
Excess cash flow can be reinvested or used to partially fund other benefits
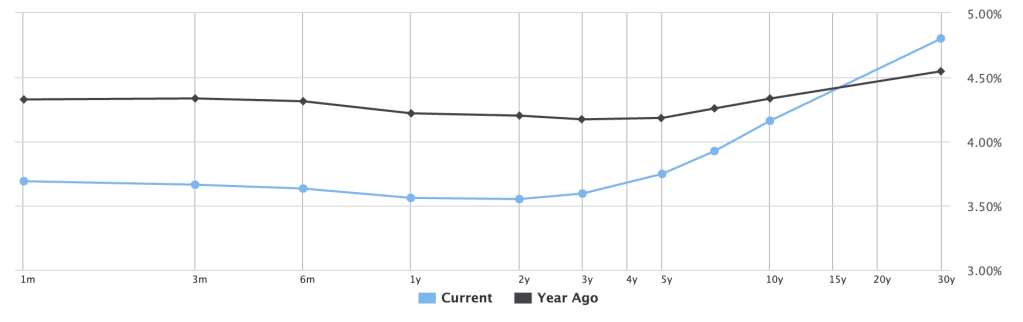
In today’s yield environment, our clients benefit to a greater extent asking us to create longer maturity programs given the steepness of the yield curve. If they don’t have the assets to fund 100% of those longer-term liabilities, we can defease a portion of them through what we call a vertical slice. That slice of liabilities can be any percentage that allows us to cover a period from next month to 30-years from now. In a recent analysis produced for a prospect, we constructed a portfolio of bonds that covered 40% of the pension plan’s liabilities out to 30-years. As a result, we reduced the present value cost to defease those liabilities by –42.7%!!
Reach out to us today to learn how much we can reduce the future value cost of your promised benefits. We do this analysis for free. We encourage you to take us up on our generous offer.