By: Russ Kamp, Managing Director, Ryan ALM, Inc.
How comforting would it be for both plan sponsors and their advisors to know how a particular strategy is going to perform over some defined period of time? I would think that having that knowledge would be quite comforting, at least as a “core” holding. Do you think that a core fixed income manager running a relative return strategy versus the Bloomberg Barclays Aggregate Index could tell you how that portfolio will perform in the next 10 1/2 years? No. Ryan ALM can with a very high degree of certainty. How’s that? Well, cash flow matching (CFM) of asset cash flows to liability cash flows locks in that relationship on the day that the portfolio is constructed. Ryan ALM views risk as the uncertainty of achieving the objective. If the true pension objective is to fund benefits and expenses in a cost-efficient manner with prudent risk, then our CFM model will be the lowest risk portfolio.
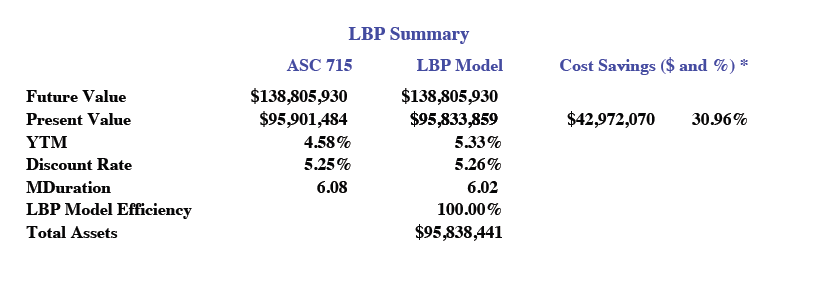
We were awarded a CFM assignment earlier this year. Our task was/is to defease the future grant payments for this foundation. On the day the portfolio was built, we were able to defease $165.1 million in FV grant payments for only $118.8 million, locking in savings (difference between FV and PV of the liability cash flows) of $46.3 million equal to 28.0% of those future grant payments. That’s fairly substantial. The YTM on that day was 5.19% and the duration was 5.92 years.
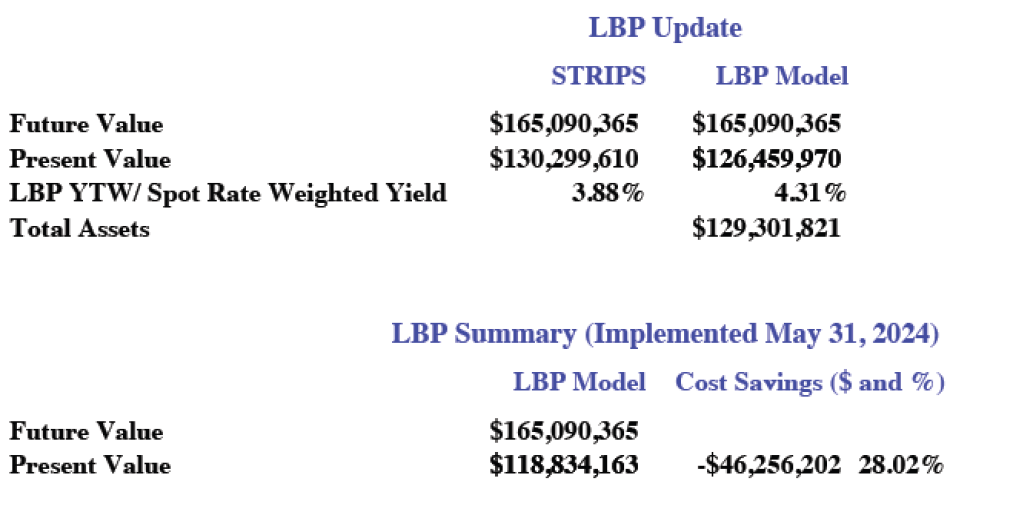
Earlier this week, we provided an update for the client through our monthly reporting. The current Liability Beta Portfolio (the name that we’ve given to our CFM optimization process) has the same FV of grant payments. On a market value basis, the portfolio is now worth $129 million, and the PV of those future grant payments is $126 million. But despite the change in market value due to falling interest rates, the cost savings are still -$46.3 million. The YTM has fallen to 4.31%, but that doesn’t change the initial relationship of asset cash flows to liability cash flows. That is the beauty of CFM.
Now, let me ask you, do you think that a core fixed income manager running a relative return portfolio can lay claim to the same facts? Absolutely, not! They may have benefitted in the most recent short run due to falling interest rates, but that would clearly depend on multiple decisions/factors, including the duration of the portfolio, changes in credit spreads, the shape of the yield curve, the allocation among corporates, Treasuries, agencies, and other bonds, etc. Let’s not discount the direction of future interest rate movements and the impact those changes may have on a bond strategy. In reality, the core fixed income manager has no idea how that portfolio will perform between now and March 31, 2035.
Furthermore, will they provide the necessary liquidity to meet those grant payments or benefits and expenses, if it were a DB pension? Not likely. With a yield to maturity of 4.31% and a market value of assets of $129.3 million, they will produce income of roughly $5.57 million/year. The first year’s grant payments are forecast to be $9.7 million. Our portfolio is designed to meet every $ of that grant payment. The relative return manager will be forced to liquidate a portion of their portfolio in order to meet all of the payments. What if rates have risen at that point. Forcing liquidity in that environment will result in locking in a loss. That’s not comforting.
CFM portfolios provide the client with the certainty of cash flows when they are needed. There is no forced selling, unlike the relative return manager that might be forced to sell in a market that isn’t conducive to trading. Furthermore, a CFM mandate locks in the cost savings on day 1. The assets not used to meet those FV payments, can now be managed more aggressively since they benefit from more time and aren’t going to be used to meet liability cash flows.
Asset allocation strategies should be adapted from a single basket approach to one that uses two baskets – liquidity and growth. The liquidity bucket will house a defeased bond portfolio to meet all the cash flow requirements and the remainder of the assets will migrate into the growth bucket where they can now grow unencumbered. You’ll know on day 1 how the CFM portfolio is going to perform. Now all you have to worry about are those growth assets, but you’ll have plenty of time to deal with any challenges presented.