By: Russ Kamp, CEO, Ryan ALM, Inc.
I recently read an article by Cliff Asness of AQR fame, titled “2035: An Allocator Looks Back over the Last 10 Years”. It was written from the perspective that performance for world markets was poor and his “fund’s” performance abysmal during that 10-year timeframe. His take-away: we can always learn from our mistakes, but do we? He cited some examples of where he and his team might have made “mistakes”, including:
Public equity – “It turns out that investing in U.S. equities at a CAPE in the high 30s yet again turned out to be a disappointing exercise”.
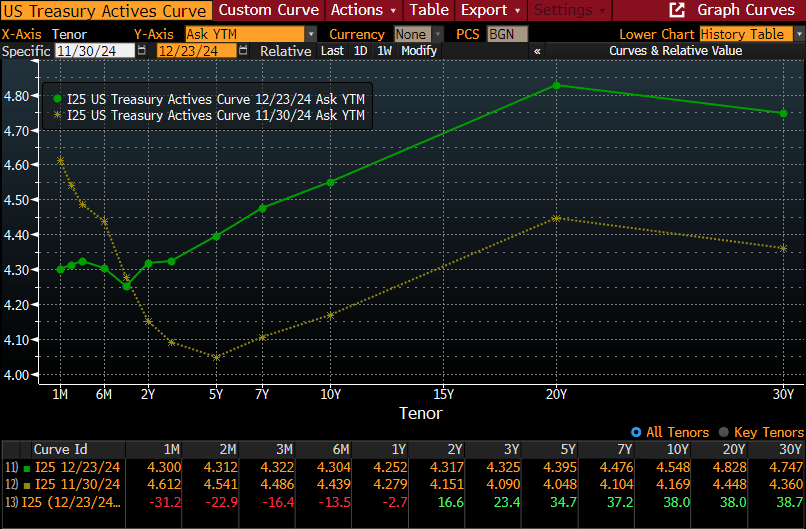
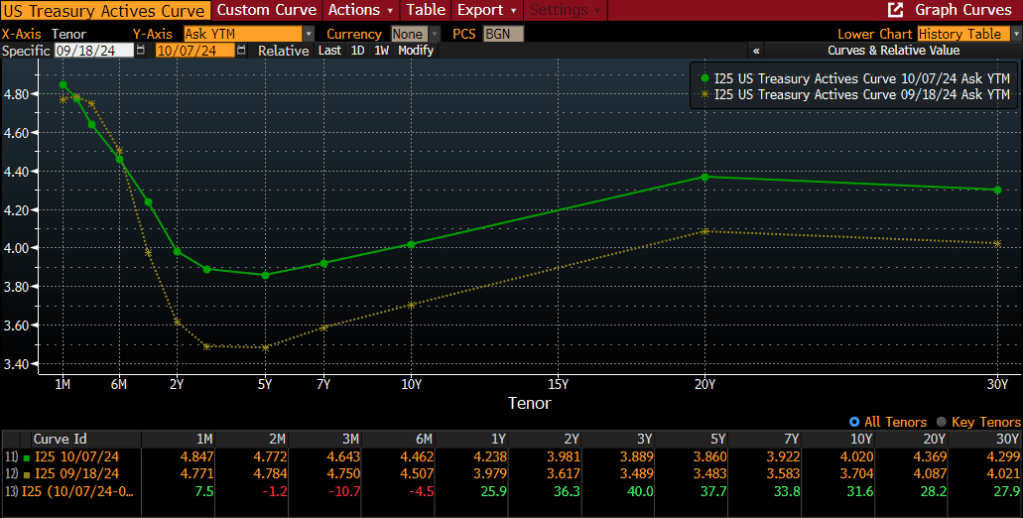
Bonds – “Inflation proved inertial” running at 3-4% for the decade producing lower real returns relative to the long-term averages.
International equities – “After being left for dead by so many U.S. investors, the global stock market did better with non-U.S. stocks actually outperforming”.
Private equity – “It turned out that levered equities are still equities even if you only occasionally tell your investors their prices”. When everyone is engaged in pursuing the same kind of investment there is a cost.
Private credit – “The final blow was when it turned out that private credit, the new darling of 2025, was just akin to really high fee public credit” Have we learned nothing from our prior CDO debacle?
Crypto – “We had thought it quite silly that just leaving computers running for a really long time created something of value”. “But when Bitcoin hit $100k we realized that we missed out on the next BIG THING” (my emphasis) “Today, 10 after our first allocation and 9 years after we doubled up, Bitcoin is at about $10,000.”
Asness also commented on active management, liquid alts, and hedge funds. His conclusion was that “the only upside of tough times is we can learn from them. Here is to a better 2035-2045”
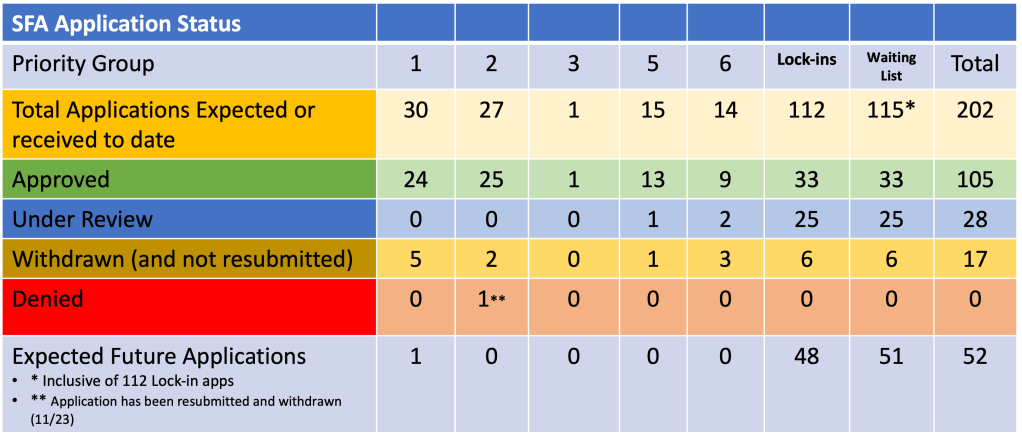
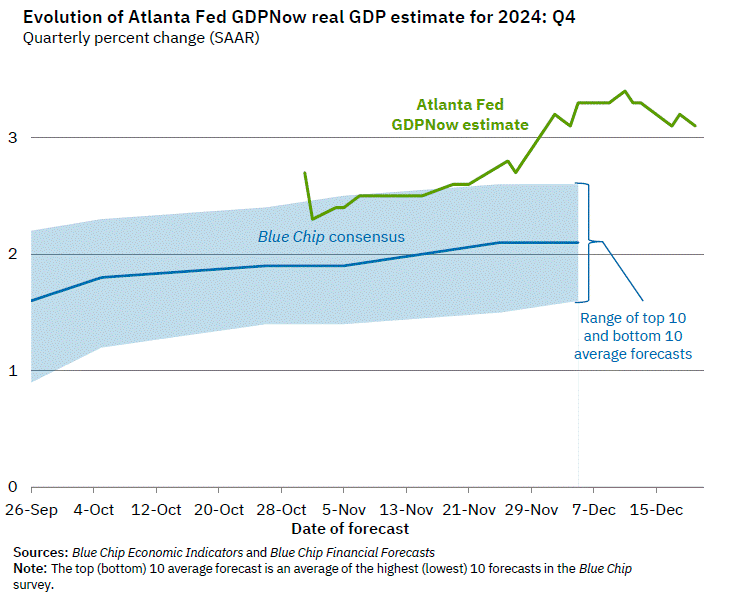
Fortunately, you reside in the year 2025, a year in which U.S. equities are incredibly expensive, U.S. inflation may not be tamed, U.S. bonds will likely underperform as interest rates rise, the incredible push into both private equity and credit will overwhelm future returns, and let’s not discuss cryptos, which I still don’t get. Question: Are you going to maintain the status quo, or will you act to reduce these risks NOW before you are writing your own 10 year look back on a devastating market environment that has set your fund back decades?
As we preach at Ryan ALM, Inc., the primary objective when managing a DB pension plan is to SECURE the promised benefits at a reasonable cost and with prudent risk. Continuing to invest today in many segments of our capital markets don’t meet the standard of low cost or of a prudent nature. Now is the time to act! It really doesn’t necessitate being a rocket scientist. Valuations matter, liquidity is critical, high costs erode returns, and no market outperforms always! Take risk off the table, buy time for the growth assets to wade through the next 10-years of choppy markets, and SECURE the promised benefits through a cash flow matching (CFM) strategy that ensures (barring defaults) that the promised benefits will be paid when due.
Thanks, Cliff, for an excellent article!