By: Russ Kamp, CEO, Ryan ALM, Inc.
The Federal Reserve meeting notes have been published, and there seems to be little appetite among the Fed Governors to reduce U.S. interest rates at the next meeting. They continue to believe that the recently inflated tariffs and current trade policy actions could lead to greater inflationary pressures. These notes do not support the current administration’s push to see the Fed Funds Rate dropped significantly – perhaps as much as 3%.
In a very informative Bloomberg post from this morning, John Authers reminded everyone that President Trump selected Jerome Powell over John Taylor, Stanford University, in 2017 to become Chairman of the Federal Reserve. I must admit that I didn’t remember that being the case, while also not recalling that it is John Taylor who is credited with developing the Taylor Rule in 1993. When I think of famous Taylors, John isn’t at the top of my list. I might have believed that it had something to do with Lawrence Taylor’s dominance on the football field where he “ruled” for 13 Hall of Fame seasons and is considered by many the greatest defensive player in NFL history (yes, I am a Giants’ fan).
So, what is the Taylor Rule? The Taylor Rule is an economic formula that provides guidance on how central banks, such as the Federal Reserve, should set interest rates in response to changes in inflation and economic output. The rule is designed to help stabilize an economy by systematically adjusting the central bank’s key policy rate based on current economic conditions. It is designed to take the “guess work” out of establishing interest rate policy.
The Taylor rule suggests that the central bank should raise interest rates when inflation is above its target (currently 2%) or when GDP is growing faster than its estimated potential (overheating). Conversely, it suggests lowering interest rates when inflation is below target or when GDP is below potential (economy is underperforming). Ironically, President Trump’s dissatisfaction with Jerome Powell’s reluctance to reduce rates given significant economic uncertainty, may have been magnified by John Taylor’s model, which would have had rates higher at this time as reflected in the graph below.
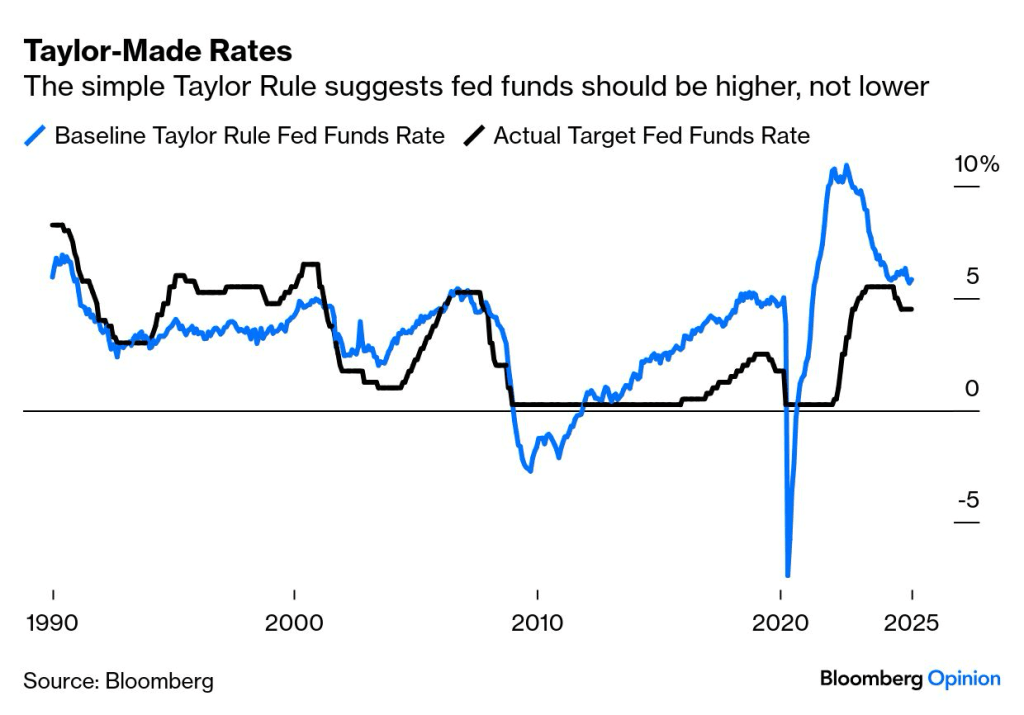
As a reminder, Ryan ALM, Inc. does not forecast interest rates as part of our cash flow matching (CFM) strategy. In fact, the use of CFM to defease pension liabilities (benefits and expenses (B&E)) eliminates interest rate risk once the portfolio is built since future values (B&E) aren’t interest rate sensitive. That said, the currently higher rate environment is great for pension plan sponsors who desire to bring an element of certainty to the management of pensions which tend to live in a very uncertain existence. By funding a CFM portfolio, plan sponsors can ensure that proper liquidity is available each month of the assignment, while providing the residual assets time to grow. There are many other benefits, as well.
Since we don’t know where rates are likely to go, we highly recommend engaging a CFM program sooner rather than later before we find that lower interest rates have caused the potential benefits (cost savings) provided by CFM to fall.
