By: Russ Kamp, CEO, Ryan ALM, Inc.
Not surprisingly, the U.S. Federal Reserve’s FOMC lowered rates another 25 bps today. The new target is 3.75%-4.0%, down from 4.5%-4.75% during the last 3 meetings. Currently, the 10-year Treasury yield (4.145% at 3:21 pm EST) is only marginally greater than the median CPI (Latest reading from the Cleveland Fed is 3.5% annually).
Ryan ALM, Inc.’s Head Trader, Steve DeVito put together the following comparison.
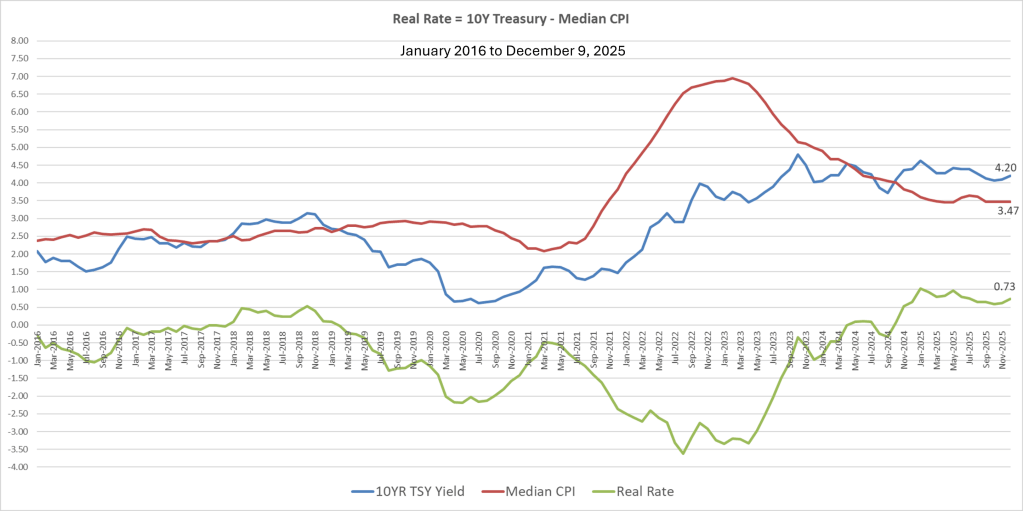
Steve is comparing the 10-year Treasury note yield (blue) versus the Median CPI (red) since January 2016. The green line is the “real” yield (10-year Treasury – the median CPI). For this period of time, there has been very little real yield, as U.S. rates were driven to historic lows before inflation spiked due to Covid-19 factors. However, historically (1962-2025), the real yield has average 2%. With rates down and inflation remaining stubbornly steady to increasing slightly, the real yield that investors are willing to take is, and has been, quite modest (0.17% since 2008). Why? Were the historically low rates in reaction to covid-19 an anomaly, or has something changed from an investor standpoint? Given today’s fundamentals, one might assume that investors are anticipating a sudden reversal in inflation, but is that a smart bet?
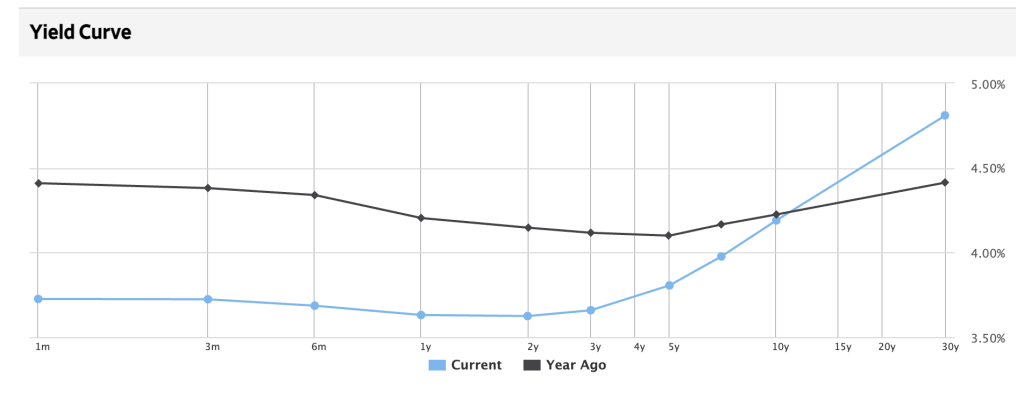
The WSJ produced the graph in today’s edition highlighting the change in the U.S. Treasury yield curve during the last year. As one can clearly see, the yield curve has gotten much steeper with the 30-year Treasury bond yield 0.4% above last year’s level (at 4.81%). That steepness would indicate to me that there is more risk longer term from inflation potentially rising.
So, it seems as if something has to give. If inflation remains at these levels, the yield on the 10-year Treasury note should be about 1.25% greater than today. If in fact, yields were to rise to that level, active core fixed income managers would see significant principal losses. However, cash flow matching managers and their clients would see the potential for greater cost reduction in the defeasing of pension liabilities, especially for longer-term programs. Bond math is very straight forward. The longer the maturity and the higher the yield, the greater the cost savings.
Managing a pension plan should be all about cash flows. That is asset cash flows versus liability cash flows of benefits and expenses. Higher yields reduce the future value of those promises. Remember, a CFM strategy is unique in that it brings an element of certainty (barring a default) to the management of pensions which live in a world of great uncertainty. Aren’t you ready for a sleep-well-at-night strategy?