By: Russ Kamp, CEO, Ryan ALM, Inc.
Managing fixed income (bonds) can be challenging as there are a plethora of risks that must be evaluated including, but not limited to, credit, liquidity, maturity/duration, yield, prepayment and reinvestment risk, etc. within the investment-grade universe. But the greatest risk – uncertainty – remains interest rate risk. Who really knows the future direction of rates? As the graph below highlights, U.S. interest rates have moved in long-term secular trends with numerous reversals along the way. Does that mean that we are headed for a protracted period of rising rates similar to what was witnessed from 1953 to 1981 or is this a head fake along the path to historically low rates?
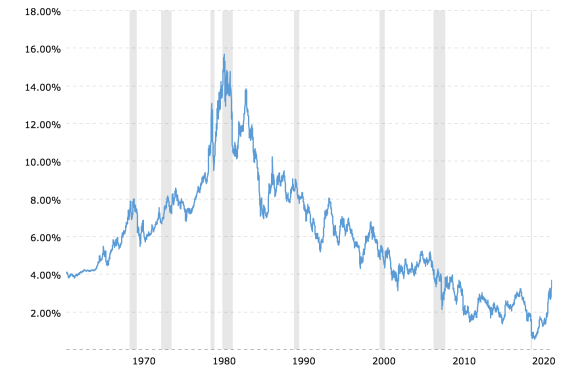
When rates are falling, it is very good for bonds as they not only capture the coupon, but they get some capital appreciation, too. However, when rates rise, it is a very different game. Yes, rising interest rates are very good for pension funds from a liability perspective, as the present value (PV) of those future benefit payments (I.e. liabilities) is reduced, but the asset side may be hurt and not only for bonds but other asset classes as well.

This is the primary reason why bonds should be used for their cash flows of interest and principal and not as a performance generator. The cash flows should be used to meet monthly benefits and expenses chronologically through a cash flow matching strategy (CFM). Unfortunately, Bonds are frequently used for performance and perhaps diversification benefits while compared to a generic index, such as the BB Aggregate index, which doesn’t reflect the unique characteristics of the pension plan’s liabilities.
U.S. interest rates are presently elevated but aren’t high by historic standards. However, the current level of rates does provide the plan sponsor with a wonderful opportunity to take risk from their traditional asset allocation by defeasing a portion of the plan’s liabilities from next month out as far as the allocation will cover. While the bond portfolio is funding monthly obligations, the remaining assets can just grow unencumbered.
Given the uncertainty regarding the current inflationary environment, betting that U.S. rates will fall making a potential “investment” in bonds more lucrative is nothing short of a crapshoot. Investing in a CFM strategy helps to mitigate interest rate risk as future values are not interest rate sensitive.
