By: Russ Kamp, CEO, Ryan ALM, Inc.
I’ve published many posts on the impact of uncertainty on the well-being of individuals and our capital markets. In neither case are the outcomes positive.
What we are witnessing in the last several trading days is the direct result of policy flip-flopping that is creating abundant uncertainty. As a result, the business environment is deteriorating. One can argue the merits of tariffs, but it is the flip-flopping of these policy decisions that is wreaking havoc. How can a business react to these policies when they change daily, if not hourly.
The impact so far has been to create an environment in which both investment and employment have suffered. Economic uncertainty is currently at record levels only witness during the pandemic. Rarely have we witnessed an environment in which capital expenditures are falling while prices are increasing, but that is exactly what we have today. Regrettably, we are now witnessing expectations for rising input prices, which track consumer goods inflation. It has been more than four decades since we were impacted by stagflation, but we are on the cusp of a repeat last seen in the ’70s. How comfortable are you?
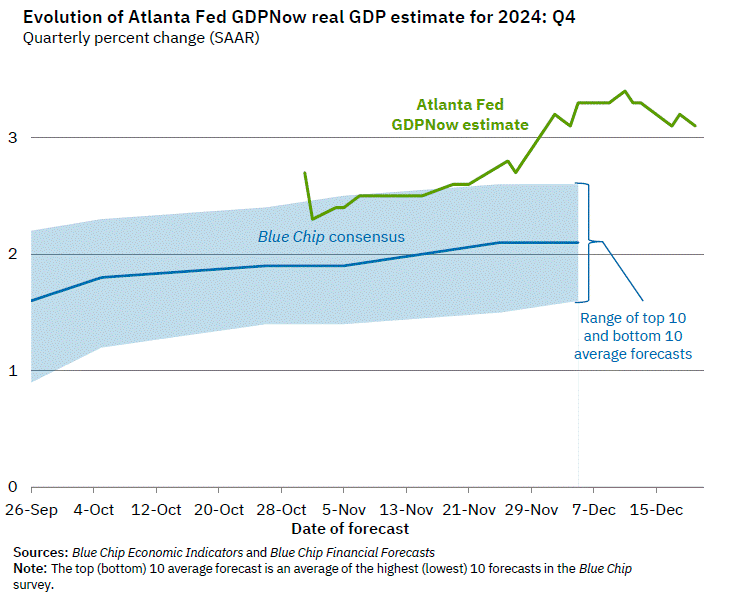
We just got a glimpse of how bad things might become for our economy when the Atlanta Fed published a series of updates driving GDP growth expectations down from a high of +3.9% earlier in the quarter to the current -2.4% published today. The key drivers of this recalibration were trade and consumer spending. The uncertainty isn’t just impacting the economy. As mentioned above, our capital markets don’t like uncertainty either.
I had the opportunity to speak on a panel last week at Opal/LATEC discussing Risk On or Risk Off. At that point I concluded that little had been done to reduce risk within public pension plans, as traditional asset allocation frameworks had not been adjusted in any meaningful way. It isn’t too late to start the process today. Action should be taken to reconfigure the plan’s asset allocation into two buckets – liquidity and growth. The liquidity bucket will provide the necessary cash flow in the near future, while buying time for the growth assets to wade through these troubled waters. Doing nothing subjects the entire asset base to the whims of the markets, and we know how that can turn out.